Sai Konan* and Ritwik Kejriwal
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Taranaki Base Hospital, New Plymouth, New Zealand
*Corresponding author: Sai Konan, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Taranaki Base Hospital, New Plymouth, New Zealand.
E-mail: saikonan3@gmail.com
Received: November 29, 2025; Accepted: December 10, 2025; Published: December 24, 2025
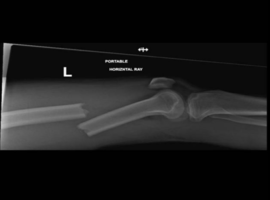
Citation: Konan S, Kejriwal R. Femoral Shaft Fracture with Ipsilateral Knee Dislocation and Popliteal Artery Occlusion: A Case Report. Case Rep Orthop Surg J. 2025; 4(4): 155.